Liposomes
Experience Makes the Difference
TTY has specialized in the field of liposomes utilizing the hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions for more than 20 years. Our products include Lipo-Dox® (Liposomal Doxorubicin Injection) and Lipo-AB® (Liposomal Amphotericin B) and have received Taiwan FDA approval in 1998 and 2013. Our pharmaceutical development team continues to develop high barrier generics and novel drugs.
Parenteral manufacturing can be a complicated process. Cytotoxics, Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs), highly potent compounds, biologics, and lyophilized products present many challenges and require specialized understanding and expertise. TTY brings longevity of experience in handling complex sterile manufacturing challenges.
TTY has specialized in the field of liposomes utilizing the hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions for more than 20 years. Our products include Lipo-Dox® (Liposomal Doxorubicin Injection) and Lipo-AB® (Liposomal Amphotericin B) and have received Taiwan FDA approval in 1998 and 2013. Our pharmaceutical development team continues to develop high barrier generics and novel drugs.
Parenteral manufacturing can be a complicated process. Cytotoxics, Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs), highly potent compounds, biologics, and lyophilized products present many challenges and require specialized understanding and expertise. TTY brings longevity of experience in handling complex sterile manufacturing challenges.
TTY Specializes in Injectable Liposomal Formulations
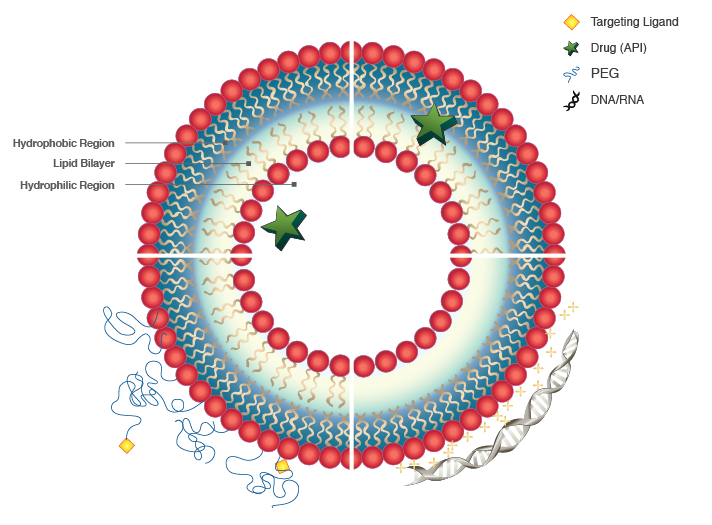
Liposomes are unilamellar vesicles formed by phospholipids, with particle sizes ranging from 30 nm to 500 nm. The pharmacokinetic profile of liposomes is affected by their size, surface charge, and physical-chemical properties.
Liposomes are bilayer vesicles with both a hydrophilic core and hydrophobic surface made by hydration of phospholipids. Their distinctive shape provides liposomes the ability to encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs.
Liposomes are unilamellar vesicles formed by phospholipids, with particle sizes ranging from 30 nm to 500 nm. The pharmacokinetic profile of liposomes is affected by their size, surface charge, and physical-chemical properties.
Liposomes are bilayer vesicles with both a hydrophilic core and hydrophobic surface made by hydration of phospholipids. Their distinctive shape provides liposomes the ability to encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs.
|
|
Encapsulated in Hydrophilic Region
|
Encapsulated in Hydrophobic Region
|
Liposomes with Targeting Ligand
|
Encapsulated with Macromolecules
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | |
| ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | |
| ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | |
| ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | |
| ◎ | ||||
| ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | |
| ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ |
Liposomes that Encapsulate Drugs in the Hydrophilic Region
Hydrophilic drugs are retained within the aqueous core area of liposomes. For example, Liposomal Doxorubicin Injection is liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin within the hydrophilic pocket and coated with PEG (polyethylene glycol) to evade detection and destruction by the immune system. The PEG coating improves the stability and lengthens the half-life in the circulation. Our first liposome product, Lipo-Dox ®, is in this category.
Hydrophilic drugs are retained within the aqueous core area of liposomes. For example, Liposomal Doxorubicin Injection is liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin within the hydrophilic pocket and coated with PEG (polyethylene glycol) to evade detection and destruction by the immune system. The PEG coating improves the stability and lengthens the half-life in the circulation. Our first liposome product, Lipo-Dox ®, is in this category.
- Commercial production:
Liposomes that Encapsulate Drugs in the Hydrophobic Region
Hydrophobic drugs are situated within the hydrophobic region of the bilayer. For example, Liposomal Amphotericin B injection (Lipo-AB®) is composed of liposomes containing amphotericin B (AmB) intercalated within the membrane. AmB is an effective but toxic antifungal drug, known to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, presumably by assembling into transmembrane pores in a sterol-dependent manner. The aggregation of AmB molecules in a phospholipid bilayer is crucial for the drug's activity. Liposomal preparations of AmB have the advantage of lower toxicity compared with conventional preparations.
Hydrophobic drugs are situated within the hydrophobic region of the bilayer. For example, Liposomal Amphotericin B injection (Lipo-AB®) is composed of liposomes containing amphotericin B (AmB) intercalated within the membrane. AmB is an effective but toxic antifungal drug, known to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, presumably by assembling into transmembrane pores in a sterol-dependent manner. The aggregation of AmB molecules in a phospholipid bilayer is crucial for the drug's activity. Liposomal preparations of AmB have the advantage of lower toxicity compared with conventional preparations.
- Commercial production:
Liposomes that Contain Targeting Ligands
Although clinically useful antitumor activity has been demonstrated with passively targeted liposomes, an additional level of sophistication and specificity for tumor cells can be achieved through ligand-mediated targeting, also known as active targeting. This involves the coupling of targeting ligands such as monoclonal antibodies, antibody fragments, proteins, and peptides to the surface of a liposome to selectively target tumor cells that overexpress a particular cell surface receptor. Active targeting of liposomes can significantly increase the amount of drug delivered to the target cell compared to delivery of the free drug or passively targeted liposomes.
Although clinically useful antitumor activity has been demonstrated with passively targeted liposomes, an additional level of sophistication and specificity for tumor cells can be achieved through ligand-mediated targeting, also known as active targeting. This involves the coupling of targeting ligands such as monoclonal antibodies, antibody fragments, proteins, and peptides to the surface of a liposome to selectively target tumor cells that overexpress a particular cell surface receptor. Active targeting of liposomes can significantly increase the amount of drug delivered to the target cell compared to delivery of the free drug or passively targeted liposomes.
Liposomes that encapsulate Macromolecules
Cationic liposome-DNA complexes are regarded as promising materials for safe and efficient delivery of genes for therapeutic applications. Cationic liposomes react spontaneously with the negatively charged DNA molecules (self-assembling system), forming complexes with DNA molecules participating in the reaction.
Cationic liposome-DNA complexes are regarded as promising materials for safe and efficient delivery of genes for therapeutic applications. Cationic liposomes react spontaneously with the negatively charged DNA molecules (self-assembling system), forming complexes with DNA molecules participating in the reaction.